Neuroprosthesis for Improving Dynamic Trunk Stability
Milos Popovic, Kei Masani
The stability of trunk is critical in individuals with spinal cord injury. In fact, individuals with paraplegia and quadriplegia as a result of spinal cord injury often value regaining trunk stability more than regaining the ability to walk. We have been investigating the biomechanics of trunk and have used this knowledge to investigate the utility of functional electrical stimulation (FES) on improving dynamic trunk stability in this population. We have revealed the synergy of trunk muscles in individuals with spinal cord injury and have demonstrated how FES can be used to improve trunk stability.
Project Publications
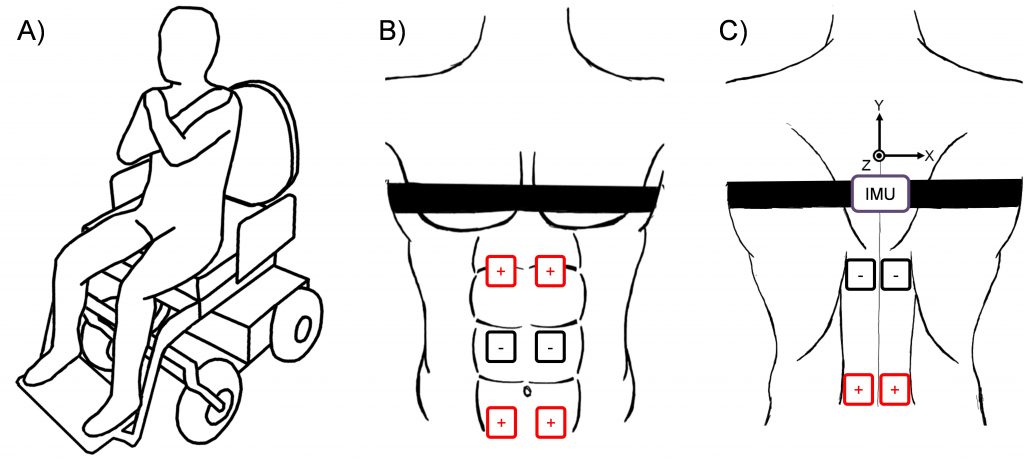
- Patel K, Milosevic M, Nakazawa K, Popovic MR, Masani K. Wheelchair neuroprosthesis for improving trunk stability. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 25(12): 2472-2479, 2017.
- Milosevic M, Shinya M, Masani K, Patel K, McConville KMV, Nakazawa K, Popovic MR. Anticipation of direction and time of perturbation modulates the onset latency of trunk muscle responses during sitting perturbations. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology 26:94-101, 2016.
- Milosevic M, Masani K, Wu N, McConville KMV, Popovic MR. Trunk muscle co-activation using functional electrical stimulation modifies center of pressure fluctuations during quiet sitting by increasing trunk stiffness. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 12:99, 2015.
- Milosevic M, Masani K, Kuipers MJ, Rohauni H, Verrier MC, McConville KMV, Popovic MR. Trunk control impairment is responsible for postural instability during quiet sitting in individuals with cervical spinal cord injury. Clinical Biomechanics 30 (5):507-512, 2015.
- Milosevic M, Masani K, Kyan M, Popovic MR, McConville KMV. Visualization of Trunk Muscle Synergies during Sitting Perturbations using Self-Organizing Maps (SOM). IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 59 (9): 2516-2523, 2012.